What Is PTFE Syringe Filter/Teflon Syringe Filter
Polytetrafluoroethylene, abbreviated as PTFE is a polymer synthesized by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene monomers. It is white, waxy, semi-transparent, and exhibits excellent heat and cold resistance, allowing for long-term usage in the temperature range of -180 to 260ºC.
The PTFE syringe filter, also known as a Teflon filter, utilizes an internal PTFE micro-porous membrane. This material consists of micro-pores created by billions of interconnected fibers arranged in a non-concentric cross pattern. The PTFE syringe filter exhibits features including air permeability without water permeability, high air permeability, low resistance, a high particle retention rate, excellent temperature resistance, resistance to strong acids, alkalis, organic solvents, oxidizing agents, and biocompatibility.
What is Difference Between Hydrophobic PTFE Syringe Filter and Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter?
The natural PTFE membrane demonstrates hydrophobic characteristics. Despite the C-F bond being highly polar, in polytetrafluoroethylene, these bonds are symmetrically distributed, resulting in no displacement of the electron cloud. Consequently, polytetrafluoroethylene material is non-polar. Surface modification can impart hydrophilicity to it. As a result, PTFE syringe filter can be categorized into hydrophobic and hydrophilic types.
Background Information: According to the definition, when the contact angle between water and a material is <90°, the material is considered hydrophilic; when it is <10 °, the material is regarded as superhydrophilic; an angle of =0° means the material is completely wetted. Conversely, when the contact angle is >90 °, the material is considered hydrophobic, and if it’s >150 °, the material is defined as superhydrophobic.
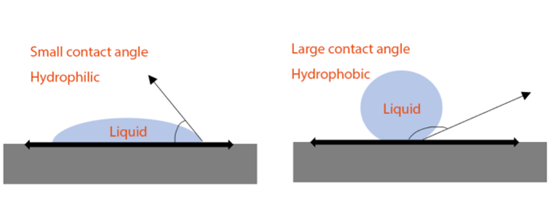
What Is Hydrophobic PTFE Syringe Filter
The internal polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane is entirely made of naturally permanently hydrophobic PTFE material, exhibiting extremely strong chemical compatibility. It is virtually capable of filtering all organic solvents and highly corrosive chemicals.
Even under very low pressure differentials, it can ensure unimpeded passage of humid air or other gases. It exhibits strong repellency to water and polar liquids, preventing droplets from adhering and forming a spherical shape.
When the pore size is larger, it also allows the passage of polar liquids such as water, but a significantly larger pressure differential is required.
Moreover, it is necessary to pre-wet with ethanol or isopropanol before aqueous solutions can be filtered through.
Applications for Hydrophobic PTFE Syringe Filter
- Widely used in the fields of chemical engineering, petrochemicals, etc., for non-polar liquids such as organic solvents, oils, and chemical reagents.
- Air monitoring and gas filtration.
What Is Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter
It has an affinity for water and polar liquids, easily adsorbing water molecules and substances containing polar functional groups. It can come into good contact with water molecules, exhibiting excellent wetting properties. Water can pass through the membrane material with minimal pressure, resulting in a significant water flux.
Applications for Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter
- Filter out particles and bacteria in bacteria liquid, gas, oil, beverage, wine, etc., and can be used for particle and bacteria inspection.
- Hydrophilic PTFE syringe filter can be used to filter aqueous solutions, most organic solutions, strong acid, and alkali solutions, and can be used as experimental sewage clarification filtration, etc.
How to Choose 0.22 μm PTFE syringe Filter or 0.45 PTFE syringe Filter?
The 0.22-micron PTFE filter and 0.45-micron PTFE filter have different membrane pore sizes, and these distinctions affect their performance and suitability in filtration and separation applications. The following are the main differences between them:
| ptfe 0.22 um filter | ptfe 0.45 um filter | |
| Pore sizes | 0.22 um | 0.45 um |
| Protein | <20000 | >20000 |
| Biobarrier performance | Effective prevention of the penetration of small organisms and bacteria | Low performance |
| Flux | Low, high pressure needed | High, low pressure needed |
| Applications | Microbial filtration. Suitable for applications requiring high microbial barrier, such as the medical industry, biopharmaceutical industry, laboratory testing, drinking water treatment, etc . | Particle removal and pre-filtration. Used in food and beverage processing, wastewater treatment, laboratory pre-filtration, etc. |
As mentioned above, you can choose a hydrophobic or hydrophilic PTFE syringe filter based on the characteristics of the sample to be filtered. Additionally, you can further decide whether to use a 0.22μm or 0.45μm filter based on the target particle size you want to remove.
-
PTFE Syringe Filters
Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter
$51.00 – $134.00Rated 0 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PTFE Syringe Filters
Hydrohobic PTFE Syringe Filter
$46.00 – $380.00Rated 0 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PTFE Syringe Filters
0.22μm Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter
$38.00 – $198.00Rated 0 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PTFE Syringe Filters
0.45μm PTFE Hydrophobic Syringe Filter
$34.00 – $1,468.00Rated 5 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PTFE Syringe Filters
0.22μm Hydrophobic PTFE Syringe Filter
$34.00 – $1,468.00Rated 5 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PTFE Syringe Filters
0.45μm Hydrophilic PTFE Syringe Filter
$38.00 – $1,608.00Rated 0 out of 5Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page