1.Institute for Agricultural Product Quality Safety and Testing Technology, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Quality Inspection and Test Center for Sugarcane and Its Product, China Ministry of Agriculture (Nanning), Nanning 530007, China
2.Biotechnology Research Institute, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Nanning 530007, China
Modern Food Science and Technology, 2022, Vol.38, No.11
Abstract: A method was developed for the simultaneous determination of 9 plant growth regulator residues ((PGRs), such as uniconazole and paclobutrazol, in whole banana fruit, banana pulp, and banana leaves by combining UPLC-MS/MS and QuEChERS syringe filter methodology, to provide a reference for the simultaneous determination of multiple PGR residues in bananas. The analytes were extracted from a sample with 1% acetonitrile acetate, and purified by a QuEChERS syringe filter; the purified sample solutions were analyzed through UPLC-MS/MS in the selective reaction monitoring (SRM) mode for the detection of uniconazole and other PGR residues in the samples. The concentrations of nine PGRs showed good linearity with the corresponding peak area in the 0.001~0.50 mg/L range, and the correlation coefficient (r2) was more than 0.9992. The average recoveries at the spiked levels of 0.05, 0.10 and 0.50 mg/kg for all target compounds in the samples were 80.50%~113.00%, with relative standard deviations (RSD) between 0.40% and 5.60%. The limits of detection (LODs, S/N = 3) for the nine PGRs ranged from 0.20 to 10.00 μg/kg, and the limits of quantification (LOQs, S/N=3), (S/N=10) ranged from 0.70 to 33.50 μg/kg. The proposed method is quick, easy, sensitive and accurate, and can be used for the simultaneous determination of the above-mentioned nine PGR residues in whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves.
QuEChERS syringe filter;
Growth Regulator Residues;
Plant growth regulators (PGRs);PGRs Residues; PGR residues, PGR residues Analysis
Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs) are a class of plant hormone compounds widely used in modern agricultural cultivation. They can promote or inhibit plant growth and regulate the processes of plant growth and development. However, if the residue levels of PGRs in bananas and banana leaves are too high, they can cause teratogenic and carcinogenic effects, affect cardiac function, and have other toxic side effects, as well as cause immeasurable harm to the ecological environment. Currently, there are no national standards in China specifying the residue limits or detection standards for PGRs in bananas. Therefore, establishing a rapid analytical method for detecting PGRs residues in banana products is of great significance.
In this experiment, a QuEChERS syringe filter was used to establish a sample pretreatment technique for multi-residue pesticide detection. This method combines the purification and filtration of the sample extraction solution in a single step, based on solid-phase extraction technology. Compared to the QuEChERS method, the multifunctional syringe filter purification method eliminates multiple steps of shaking purification and centrifugation, significantly improving detection efficiency.
Common plant growth regulators (PGRs) used in fruit and vegetable cultivation include chlormequat, mepiquat, paclobutrazol, propiconazole, uniconazole, chlorphenamidine, forchlorfenuron, flurprimidol, daminozide, brassinolide, indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-butyric acid, thidiazuron, 6-benzylaminopurine, gibberellins, and others. However, China’s national standard GB 2763-2021 “National Food Safety Standard – Maximum Residue Limits for Pesticides in Food” only specifies the residue limits and detection standards for 20 PGRs, including 2,4-D, chlormequat, 6-benzylaminopurine, cyanamide, daminozide, paclobutrazol, fluorine-containing regulators, sodium nitroprusside, mepiquat chloride, uniconazole, chlorphenamidine, forchlorfenuron, naphthaleneacetic acid, thidiazuron, trinexapac-ethyl, tetrachloronitrobenzene, calcium prohexadione, flurprimidol, ethephon, and daminozide in certain fruits and vegetables. This experiment established an analytical method for the simultaneous detection of residues of these nine PGRs in whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves using purification by multifunctional syringe filters and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS).
1 Materials and Methods
Instruments and Materials
Xevo TQ-S UPLC-MS/MS Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometer equipped with an Electrospray Ionization (ESI) source, High-Speed Tissue Homogenizer, Centrifuge.
QuEChERS syringe filter: Contain 150 mg MgSO4, 50 mg PSA, 50 mg C18

Ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (purity ≥98.0% w/w), octocrylene (purity ≥98.8% w/w), thiabendazole (purity ≥99.4% w/w); amitraz (purity ≥99.7% w/w), indole butyric acid (purity ≥99.5% w/w), indole acetic acid (purity ≥99.6% w/w), abscisic acid (purity ≥98.0% w/w), propiconazole (purity ≥99.0% w/w), chlorotoluron (purity ≥99.5% w/w), acetic acid (chromatographically pure).
1.2 Preparation of Standard Solutions
Accurately weigh appropriate amounts of the 9 analyte standard compounds and dissolve them in acetonitrile to prepare a standard stock solution with a concentration of 1,000 mg/L. Precisely transfer aliquots of the standard stock solutions and dilute with acetonitrile to prepare a standard intermediate mixed solution with a concentration of 10.0 mg/L. For use, dilute stepwise with acetonitrile or blank matrix extraction and purification solution to the required concentrations.
1.3 Sample Pretreatment Extraction: Take whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaf samples, homogenize using a tissue homogenizer to obtain a uniformly mixed sample. Weigh 10.00 g of the sample, add 20.0 mL of 1% acetic acid in acetonitrile (v/v), vortex extract for 1 minute, add 3 g of sodium chloride, vortex extract for another 1 minute, centrifuge at 4,000 rpm for 5 minutes, and collect the supernatant for further purification.
Purification: Take 1.5 mL of the above supernatant and pass it through a multi-functional needle filter into the sample vial at a rate of 2 drops per second, for UPLC-MS/MS analysis.
| 0~0.8 min | 90% A |
| 0.8~1.8 min | 90%~70% A |
| 1.8~3.8 min | 70%~50% A |
| 3.8~5.5 min | 50%~30% A |
| 5.5~7.0 min | 30%~10% A |
| 7.0~8.5 min | 10% A |
| 8.5~ 9.2 min | 10%~50% A |
| 9.2~9.6 min | 50%~90% A |
| 9.6~10.0 min | 90% |
Flow rate: 0.25 mL/min;
Injection volume: 2.0 μL.
Mass Spectrometry Conditions
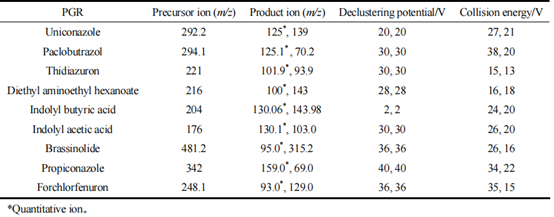
The analysis was conducted using Electrospray Ionization (ESI+) ion source and Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) mode. The desolvation gas temperature was set at 350 ℃, electrospray voltage at 3.0 kV, and ion source temperature at 150 ℃. The desolvation gas flow rate was maintained at 700 L/hr. During the instrument’s detection and analysis process, qualitative analysis was performed by comparing the information of parent ions and two daughter ions. Quantitative analysis utilized the parent ion and the daughter ion with the highest response. The MRM mode mass spectrometry parameters for the 9 plant growth regulators (PGRs) are detailed in Table 1.
Table 1 MS/MS analysis parameters for the 9 PGRs
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Instrumental Condition Optimization
2.1.1 Mass Spectrometry Condition Optimization
Due to the predominantly nitrogen-containing alkaline nature of the 9 plant growth regulators (PGRs), most of these compounds are suitable for positive ion mode (ESI+) scanning during mass spectrometry. Therefore, this experiment employed positive ion mode scanning and optimized the mass spectrometry conditions using standard solutions with concentrations of 0.1 mg/L. The optimized parent ions for ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, thiabendazole, amitraz, indole butyric acid, indole acetic acid, abscisic acid, propiconazole, and chlorotoluron were found to be m/z 292.2, 294.1, 221, 216, 204, 176, 481.2, 342, and 248.1, respectively. Other mass spectrometry parameters are detailed in Table 1.
2.1.2 Chromatographic Condition Optimization
When scanning in positive ion mode (ESI+), the addition of acid provides H+ ions to the analytes, enhancing their response in mass spectrometry. The experiment investigated the separation efficiency using methanol and acetonitrile as organic mobile phases. Acetonitrile was found to provide better peak shapes and higher responses for the 9 plant growth regulators (PGRs), therefore acetonitrile in combination with 0.1% formic acid was selected as the mobile phase. The gradient elution program of the mobile phase was optimized to achieve better separation.
Under the optimized chromatography-mass spectrometry conditions, the MRM chromatograms of ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, thiabendazole, amitraz, indole butyric acid, indole acetic acid, abscisic acid, propiconazole, and chlorotoluron spiked into a mixed blank matrix of whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves are shown in Figure 1. The retention times were 6.16, 5.73, 4.22, 3.51, 4.56, 3.75, 5.73, 6.74, and 4.95 minutes, respectively. As observed in Figure 1, the sample matrix did not interfere with the determination of the analytes.
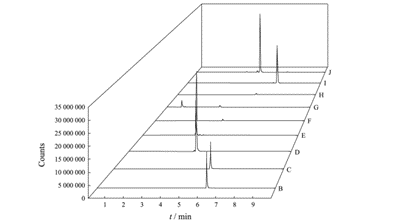
Fig.1 MRM chromatograms of 9 PGRs of mixed blank samples of banana whole fruit, banana pulp and banana leaf spiked at 0.1 mg/kg level
B – Ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate; C – Octocrylene; D – Thiabendazole; E – Amitraz; F – Indole butyric acid; G – Indole acetic acid; H – Abscisic acid; I – Propiconazole; J – Chlorotoluron
2.2 Selection of Purification Method
Extraction and purification of target compounds are crucial steps in the determination of pesticide residues in plant-derived samples, directly impacting method reproducibility and recovery rates. This study employed vortex extraction with 1% acetic acid in acetonitrile, followed by addition of sodium chloride and another vortex extraction. After centrifugation, the supernatant was directly purified using a multi-functional needle filter to adsorb interferents such as pigments and proteins. Compared to QuEChERS dispersive solid-phase extraction, this method is simpler to operate and suitable for high-throughput rapid testing requirements.
2.3 Assessment of Matrix Effects in Samples
Samples of whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves without the target PGRs were processed using the method described in section 1.3, resulting in purified solutions of blank sample matrices. These solutions were then used to gradually dilute a mixed standard solution at 10 mg/L, preparing matrix standard working solutions at concentrations of 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 mg/L. Under the optimized experimental conditions, the mass concentrations of the target compounds (X, mg/L) were used as the x-axis, with the corresponding peak areas of the quantitative ion pairs (Y) as the y-axis to construct matrix standard curves.
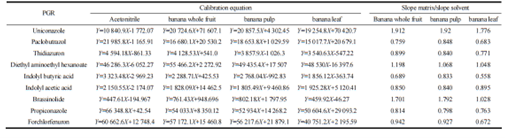
The ratio of the slope of the matrix calibration curve to that of the pure solvent calibration curve is defined as the matrix effect (ME). A ME value closer to 1 indicates a smaller matrix effect. The specific experimental results are shown in Table 2.
From Table 2, it is observed that ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate exhibits significant matrix effects (ME > 1.7) in banana peels, banana pulp, and abscisic acid in banana peels and pulp. In contrast, amitraz shows a weaker matrix effect (ME value close to 1), while other compounds demonstrate varying degrees of matrix effects. These effects may be influenced by the nature of the compounds themselves, the matrix of the samples under investigation, and the ionization efficiency of the target analytes. To minimize matrix effects, matrix calibration was employed for quantification purposes.
2.4 Linear Range, Limit of Detection, and Limit of Quantitation of the Method
Under the optimized experimental conditions described, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, thiabendazole, amitraz, indole butyric acid, indole acetic acid, abscisic acid, propiconazole, and chlorotoluron in whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves exhibit good linear relationships in the range of 0.001 to 0.5 mg/L. The matrix standard curves for the 9 plant growth regulators (PGRs) in whole bananas are illustrated in Figure 2, and the linear equations for different matrix standard curves are provided in Table 2, with correlation coefficients exceeding 0.9992.
The limits of detection (LOD) for the 9 PGRs, calculated at a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 3, are 0.50, 0.20, 0.50, 0.80, 10.00, 10.00, 3.00, 0.20, and 4.00 μg/kg, respectively. The limits of quantitation (LOQ), calculated at S/N=10, are 1.60, 0.70, 1.60, 2.50, 33.50, 33.50, 10.00, 0.80, and 13.50 μg/kg, respectively. These values meet the detection requirements for pesticide residue analysis.
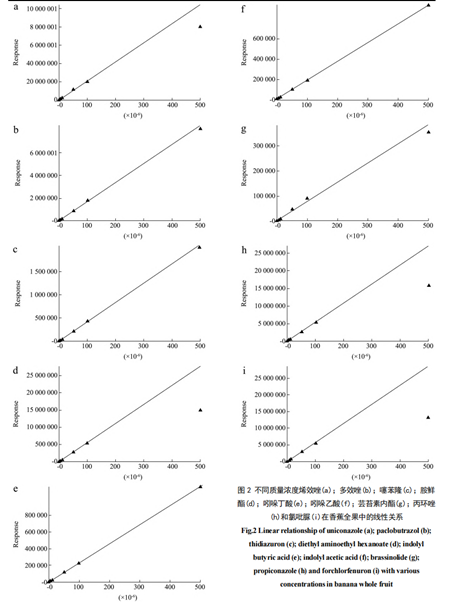
Table 2 Matrix effects of 9 PGRs in matrix of banana whole fruit, banana pulp and banana leaf
2.5 Recovery and Precision
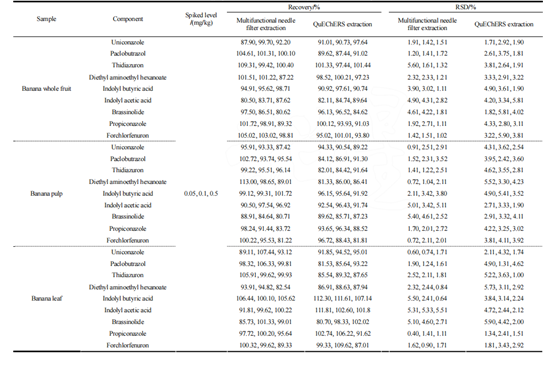
Blank samples of whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves, which did not initially contain the 9 target compounds, were used for spiked recovery experiments (comparison between QuEChERS syringe filter and QuEChERS tube). The spiked concentrations of the 9 PGRs in 10 g samples were 0.05, 0.10, and 0.50 mg/kg, respectively. The results are shown in Table 3.
In whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves, the average spiked recovery rates of this method ranged from 80.50% to 113.00%. For QuEChERS, the average spiked recovery rates ranged from 80.70% to 112.30%. The relative standard deviations (RSD) for both methods were between 0.40% and 5.60% for QuEChERS syringe filter and between 1.00% and 5.90% for QuEChERS. It is evident that both methods meet the requirements for recovery and precision.
However, the multi-functional needle filter method combines purification and filtration in one step, eliminating the need for shaking and centrifugation steps in the dispersive solid-phase extraction (QuEChERS) method. This simplifies the purification process, reduces sample preparation time, and effectively improves detection efficiency. Moreover, it efficiently removes matrix interferents such as pigments and proteins from the extraction solution. Thus, this method is simpler, quicker, and more convenient.
Table 3 Average spiked recoveries and RSD (n=6) of 9 PGRs in real samples
2.6 Detection of Actual Samples
Ten samples each of bananas and corresponding banana leaves were collected from the plantation. Following the procedures outlined in section 1.3, which involves sample preparation, the presence of ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, thiabendazole, amitraz, indole butyric acid, indole acetic acid, abscisic acid, propiconazole, and chlorotoluron was tested. It was found that none of the above-mentioned PGRs residues were detected in any of the samples.
3.Conclusion
This study established an analytical method using QuEChERS syringe filter purification coupled with ultra-high performance UPLC-MS/MS for simultaneous determination of ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene, thiabendazole, amitraz, indole butyric acid, indole acetic acid, abscisic acid, propiconazole, and chlorotoluron residues in whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves. Samples were extracted with 1% (V/V) acetic acid in acetonitrile and purified in a single step using the QuEChERS syringe filter , followed by analysis using electrospray ionization (ESI+) and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode on the mass spectrometer.
The method achieved limits of detection (LOD) ranging from 0.20 to 10.00 μg/kg and limits of quantitation (LOQ) ranging from 0.70 to 33.50 μg/kg. This method is simple, rapid, and demonstrates good accuracy, sensitivity, and precision. It is suitable for simultaneous batch analysis of ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate and 8 other PGRs residues in whole bananas, banana pulp, and banana leaves.